With the speedy leap in development of newer, better solar technology, renewable energy is sure to be making common utilities redundant in the next few years. With its unlimited advantages it is slowly becoming a force to be reckoned with the clean energy business. Locating a solar panel on a residential roof is becoming more and more common these days. Statistics show that every two and a half minutes, a residential or commercial envelop installs a new solar panel. Solar energy has been in the development stages for the past few decades and has over the years become a widely embraced public phenomenon. Governments have started investing in solar energy – sometimes in the form of entire plants, and other times in the form of individual owner sources for urban activities such as parks and highways.
With so much advancement going on in the solar energy field, it is important to know how this technology actually works. Farther down, we would be discussing just what it is that converts the sun rays into usable electricity.
READ ALSO: What Is Solar Panel Mounts
Element no. 1 – the sun
Conventional electricity generating techniques include the burning of fossil fuel, which usually comes from non-renewable sources. The burning of this fossil fuel can generate harmful gasses in the atmosphere, which can inadvertently cause environmental degradation. Most of the fodder for fossil fuels is dug out, or quarried from the mountains in the form of coal and natural gas. While coal is then burned to generate power, natural gas is distributed along pipelines that can sometimes explode. All of these endeavors are labor intensive and risky.
Solar energy on the other hand comes with no such risks. It derives its source of energy from the sun – which, lest come the apocalypse is an infinite source of power. Sunlight is a natural phenomenon, and generating usable power for daily life routines using such an infinitely renewable source is an ingenious idea. Aside from being abundant, it is obviously very easily available, and inherently ‘green’. There is no labor intensive work involved that could cause damage to the work force, or the environment. It is the purest form of renewable energy.
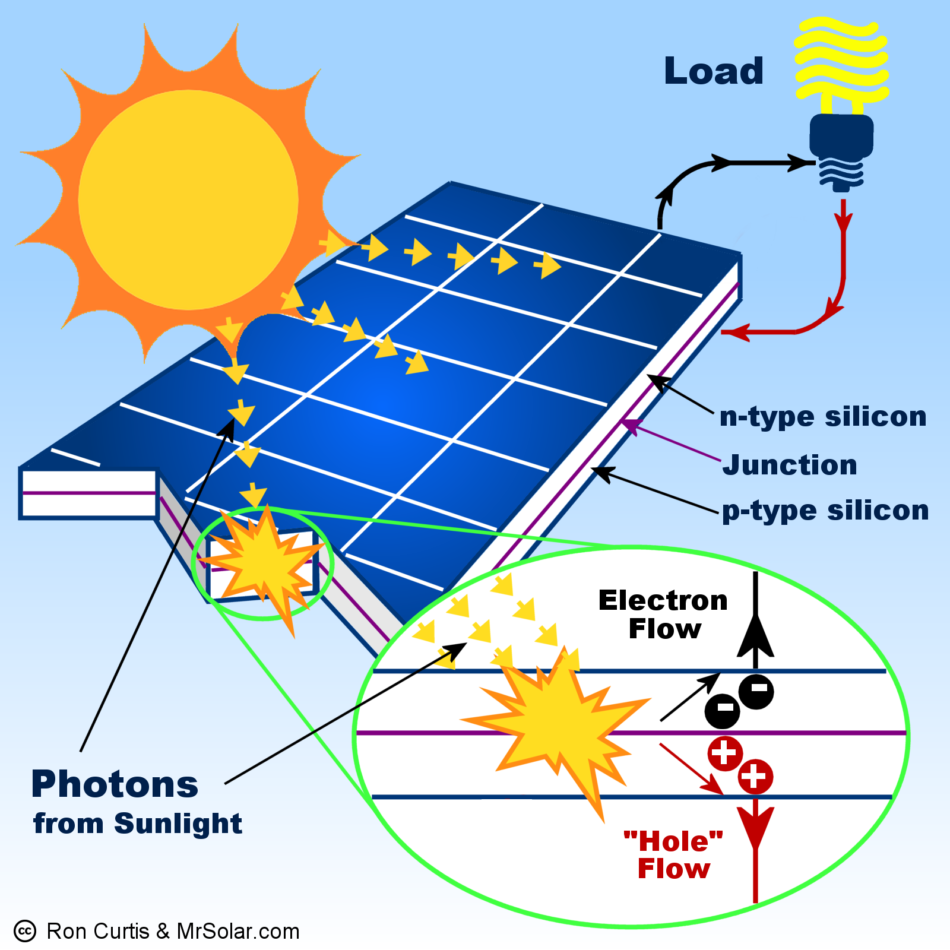
Getting the main source of energy is one aspect of this technology – the other one includes actually converting this source into usable energy. This is done by the use of photovoltaic technology. Solar energy is, in scientific and professional terms, referred to as photovoltaics or PV. It’s a relatively straightforward as well as literal terminology – where photons means light, and voltaic refers to electricity. It is a simple chemical process which is easy to understand, and is explained below.
Element no. 2 – the solar panel
It is a well-known fact that sunlight travels at the speed of light. Now when this fast paced light falls on the face of a solar panel; that is when the process of conversion actually begins.
A group of solar panels that are interconnected to get the required electric output are known as a solar array. These are typically arranged on a slanted roof when it comes to homes, but could be adapted into yards and fields, or even flat roof given they face a direct gain of ample amount of sunlight.
The structure of a solar panel is such that it resembles a flat plate wafer of glazed silicon cells, assumed in the shape of a square and is usually known as a module in layman terms. The silicon cells in its formation act as semiconductors and contain electrons. The surface of these cells are glazed with phosphorous and boron, which create a magnetic field – which, when takes effect works with a half negative and a half positive charge in the cells. When these cells are exposed to sunlight, the electrons destabilize, which makes the negatively charged electrons stick to one side of the silicon cells. This movement of electrons produces electrical charge, and the metal conductors on the cells transfer this electricity to the wires.
Element no. 3 – the Inverter
The electricity produced by the solar panels is not exactly compatible with the common grid network provided by the government authorities. It is called direct current (DC), and usually flows in a single direction. Homes are usually connected to a wiring of alternating current (AC). It has the ability to flow in more than one direction and is more beneficial for long distance range wiring.
When you connect your home with a solar panel, it is important to convert the DC into AC in order to fully power your house. For this purpose we use the solar inverter. It is a land looking metal box that should be placed near the fuse box. It is the keystone of this entire phenomenon, as it converts the direct current into alternating one.
These come with various options – there are inverters that can separate the home from the general grid in the case of a power outage, and also consists of a small battery power that can provide electricity to your home in case of a blackout.
Conclusion
Now you can better understand the workings of a solar powered system, and how it can be integrated into your home.